元旦放假通知
...
The current DVR storage architecture facilitates the input of analog video signals from the camera to the DVR card. The video capture chip converts the analog signal into a digital signal, which is then passed to the temporary memory on the card, which is then executed on the card. The compression algorithm reduces the huge video signal compression; finally these compressed video signals enter the PCI directly or through the PCI bridge chip and are stored to the hard disk.
With the rapid development of the security monitoring industry, the advantages of embedded hard disk recorders gradually emerged. On the one hand, the video resolution gradually transitions from the CIF format to the D1 format. On the other hand, the number of channels for a single DVR can reach 32 channels from 4 channels. Everything seems to be smooth, but due to the huge capacity of the D1 format and the longer storage time required by customers, the built-in hard drive capacity is difficult to meet. So to use the same capacity to store more video images, video compression technology plays a key role here.
The current DVR storage architecture facilitates the input of analog video signals from the camera to the DVR card. The video capture chip converts the analog signal into a digital signal, which is then passed to the temporary memory on the card, which is then executed on the card. The compression algorithm reduces the huge video signal compression; finally these compressed video signals enter the PCI directly or through the PCI bridge chip and are stored to the hard disk. In this way, the externally input image is encoded by the video encoding and decoding technology to remove a large amount of redundant information. The redundant information can be divided into spatial redundancy information and time domain redundancy information. The essence of compression technology coding technology is to remove the redundant information in the data. It mainly includes intraframe image data compression technology, inter picture image data compression technology and entropy coding compression technology.
First, to the time domain redundancy information
Using inter-frame coding technology can remove time-domain redundant information, mainly including the following three parts:
(I) Motion compensation
Motion compensation uses the previous partial image to predict and compensate the current partial image. It is an effective method to reduce the redundant information of the frame sequence.
(b) Movement indication
Different areas of the image need to use different motion vectors to describe the motion information. The general motion vector is compressed by coding.
(c) Motion estimation
Motion estimation extracts motion information from a video sequence.
Second, to the airspace redundancy information
Intra-space redundancy information mainly uses intra-frame coding techniques and entropy coding techniques:
(a) transform coding
Both intraframe and predictive difference signals have high spatial redundancy information. Transform coding transforms the spatial signal into another orthogonal space, which reduces its correlation and reduces data redundancy.
(b) Quantization coding
After transform coding, a batch of transform coefficients are generated, and these coefficients are quantized so that the output of the encoder reaches a certain bit rate. However, this process also leads to a decrease in accuracy.
(III) Entropy coding
Entropy coding is lossless coding. It further compresses the transformed and quantized coefficients and motion information.
Currently, the mainstream DVRs used in the market include codec technologies MPEG-2, MPEG-4, H.264, and M-JPEG. MPEG-4 and H.264 are the most common compression methods in the domestic surveillance industry.
Prior to the development of MPEG-4, MPEG-1, MPEG-2, H.261, and H.263 were all based on the first-generation compression coding technology. The encoder was designed based on the statistical characteristics of the image signal and it belongs to the category of waveform coding. MPEG-4 represents the second-generation compression/encoding technology based on model/object, and adopts a new generation of video coding technology. For the first time in the history of video coding, it expands the coding object from the image frame to a practically arbitrary shape. Objects, thereby achieving a shift from traditional pixel-based coding to modern coding based on objects and content. In addition to the core technologies of the first generation of video coding, such as transform coding, quantization, and entropy coding, MJPG-4 also proposes some new and innovative key technologies, such as video object extraction technology, VOP video coding technology, and video. Encoding scalability technology, motion estimation and motion compensation techniques.
H.264 is a high-performance video codec technology. H.264 is built on the basis of MPEG-4 technology. Its codec flow mainly includes five parts: inter-frame and intra-frame prediction, transform and de-exchange, quantization and de-quantization, loop filtering, and entropy coding. . It is the latest and most promising video compression standard since the release of the MPEG-2 video compression standard in 1995. Through this standard, the compression efficiency under the same image quality is more than 2 times higher than the previous standard, and many advanced technologies are added, such as: hierarchical design, high-precision, multi-mode motion estimation, unified VLC.
H.264 and the previous MPEG-2 and MPEG-4, the biggest advantage is a very high data compression ratio, under the same image quality conditions; H.264 compression ratio is MPEG-2 more than twice, is 1.5-2 times of MPEG-4. At the same time; the coding technology also has: accurate matching decoding, to avoid error accumulation; powerful fault tolerance; delay differential level to adapt to more application environments. Therefore, H.264 is the mainstream video coding technology of today's DVRs.
From the perspective of the current market, DVRs are low-priced, mature products, and their applications are still quite extensive. They are mainly used in projects with fewer monitoring points and lower level requirements. However, due to the performance limitations of the codec equipment, the hard disk sequential write mode is generally adopted, and RAID redundancy technology is not used to implement data protection. With the ever-increasing hard disk capacity, the chance of a single-disk failure leading to the loss of critical data is increasing at the same time. Most DVRs only have 4 to 8 hard disks, so the capacity is very small and the compatibility is poor. Monthly monitoring data requirements; In addition, the DVR architecture does not have the capacity for flexible expansion, or even unable to expand, resulting in limited hard drive capacity can not meet the growing needs of users.
With the continuous increase in market demand, the future DVR will develop around the following aspects:
(1) Higher resolution.
At present, high-end DVRs generally have D1 encoding effects, but they are still in the development stage. I believe that in the future there will be a clear and high-definition encoding technology that can take into account network transmission. This, of course, depends on the development of hard disk capacity, as well as changes in network bandwidth and cost.
(2) More rich features.
The need for a richer software interface facilitates the access of large-scale systems and forms a comprehensive monitoring system, which will further facilitate the application and popularization of products.
(3) Better environmental adaptability.
The monitoring environment is generally more complex. In terms of temperature, the difference may be -20 degrees Celsius to 50 degrees Celsius, which requires the DVR to adapt to various environments and have better performance.
(4) The equipment is more intelligent.
Such as using biometrics, behavior analysis technology, video search technology and other intelligent technologies to make equipment more intelligent, to achieve video surveillance from passive defense to active prediction.
In summary, the current video surveillance system mainly develops in two directions: First, the DVR will do more "precision" in terms of product performance and humanization, making the DVR more widely used in all areas of the security industry. The second is that DVR will support and match more products and equipments, compete with NVR for development, and serve the development of video surveillance industry.

...

公司全体员工根据《国务院办公厅关于2023年部分节假日安排的通知》,公司五一国际劳动节放假安排通知如下:今年劳动节4月29日至5月3日放假 ...

艾草幽香,龙舟竞渡,今又端午!为庆祝这个千年传统佳节,提前祝大家节日快乐。现就端午节放假作如下通知: 1、端午节放假共3天,6月3 ...
...
...
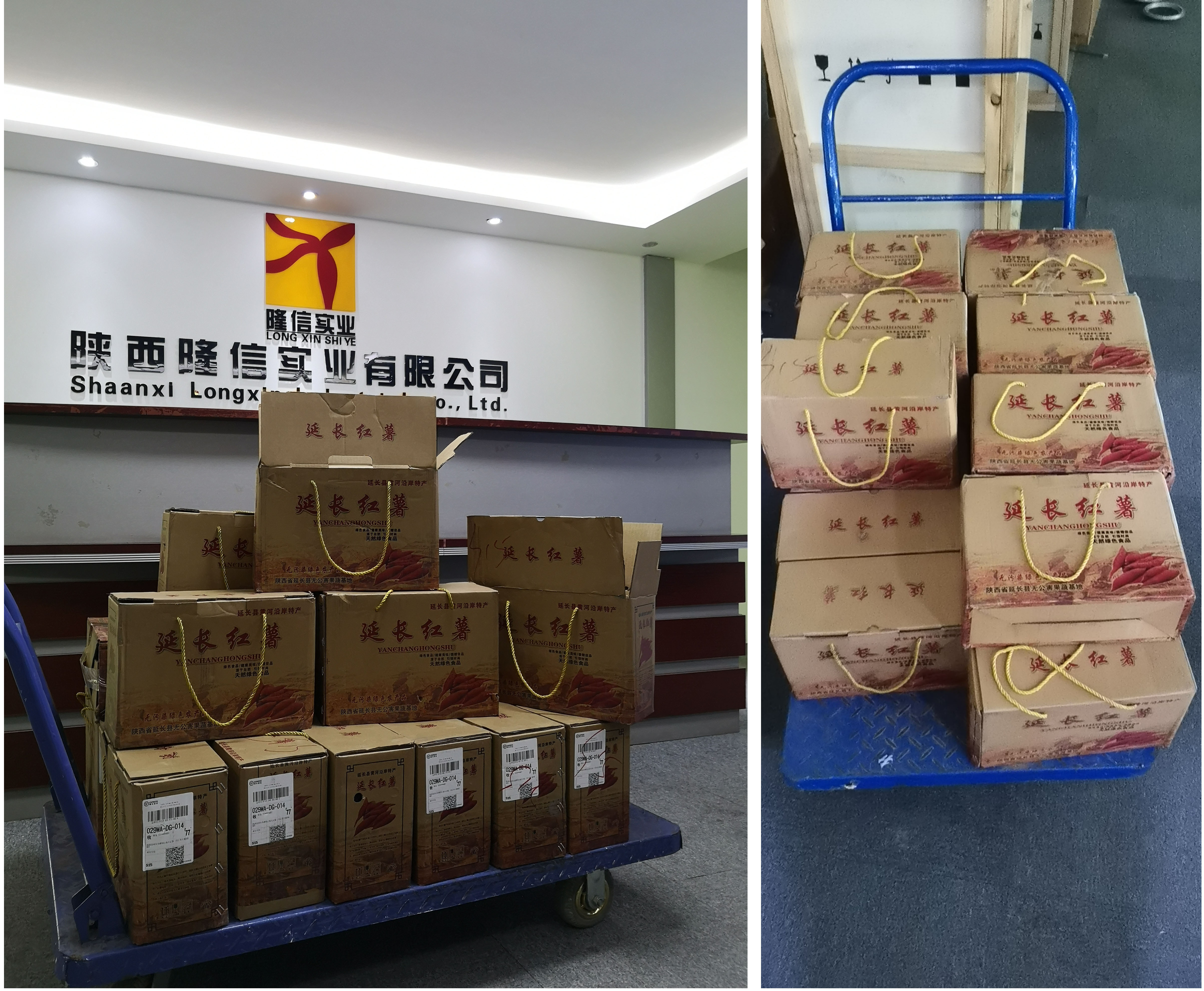

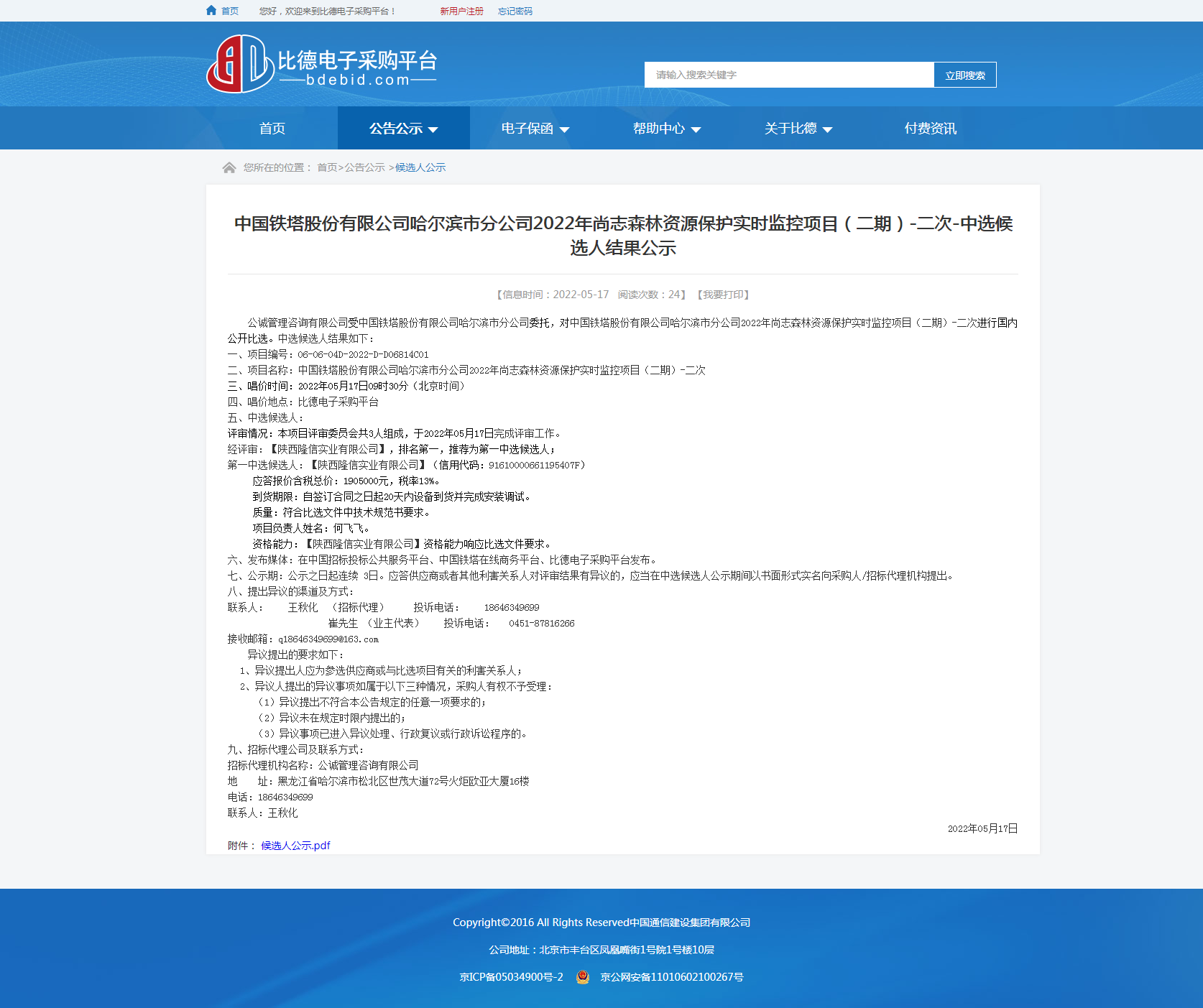
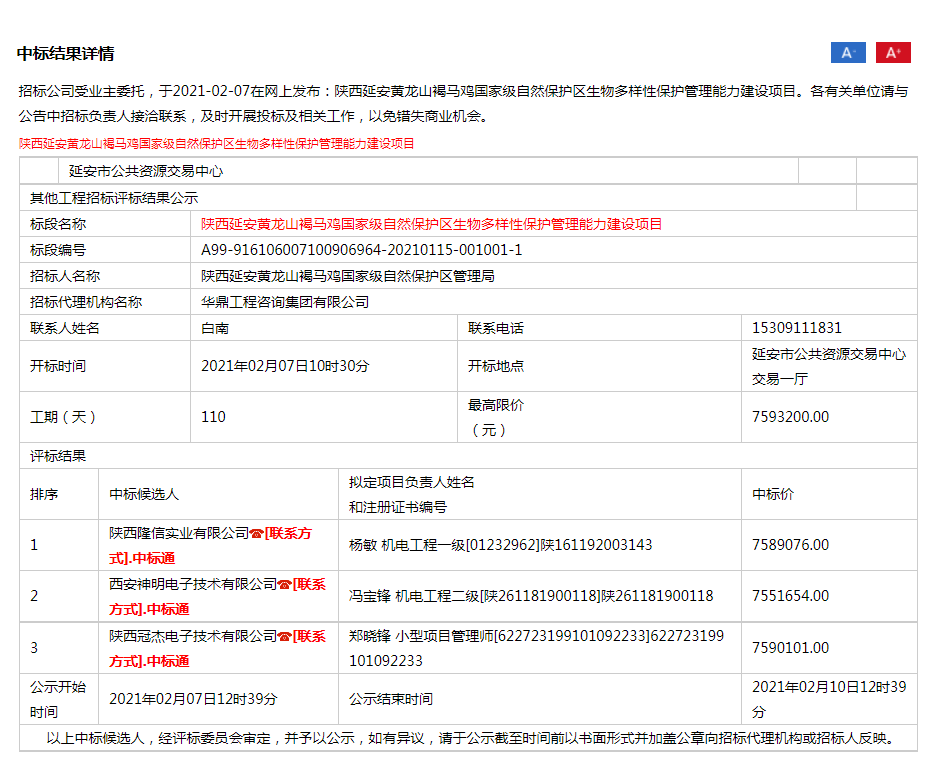
我公司主营为国家森林防火监控项目,自接到陕西省森林资源管理局,关于帮助延长县黑家堡镇贺家沟村扶贫点贫困户红薯滞销问题,我公司积极响 ...

2020年隆信十佳照片,经过大家踊跃投稿,积极投票现已选出。我们征集照片的意义旨在建立企业风采,进行公司文化宣传,以及之后工作需要。由 ...

12月2日,第四届全国森林消防装备展会暨应急救援装备展在广东深圳坪山燕子湖国际会展中心举办。本届展会由中国林学会森林与草原防火专业委 ...